Acute Myocardial Infarction (MI)
Acute myocardial infarction is resulting from acute obstruction of a coronary artery
SIGNS and SYMPTOMS:usually begin suddenly.
There are:
- Chest pain or discomfort. This is often described as aching, pressure, tightness, or burning.
- Pain that starts in the chest and spreads to other parts of the body including the shoulders, arms, upper belly area, back, neck, or jaw.
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Indigestion.
- Shortness of breath, also called dyspnea.
- Sudden, heavy sweating.
- Racing heartbeat.
- Feeling lightheaded or dizzy.
- Fainting.
- Unusual fatigue.

How to diagnosis?
Acute coronary syndrome often causes severe chest pain or discomfort. It is a medical emergency that needs a diagnosis and care right away.
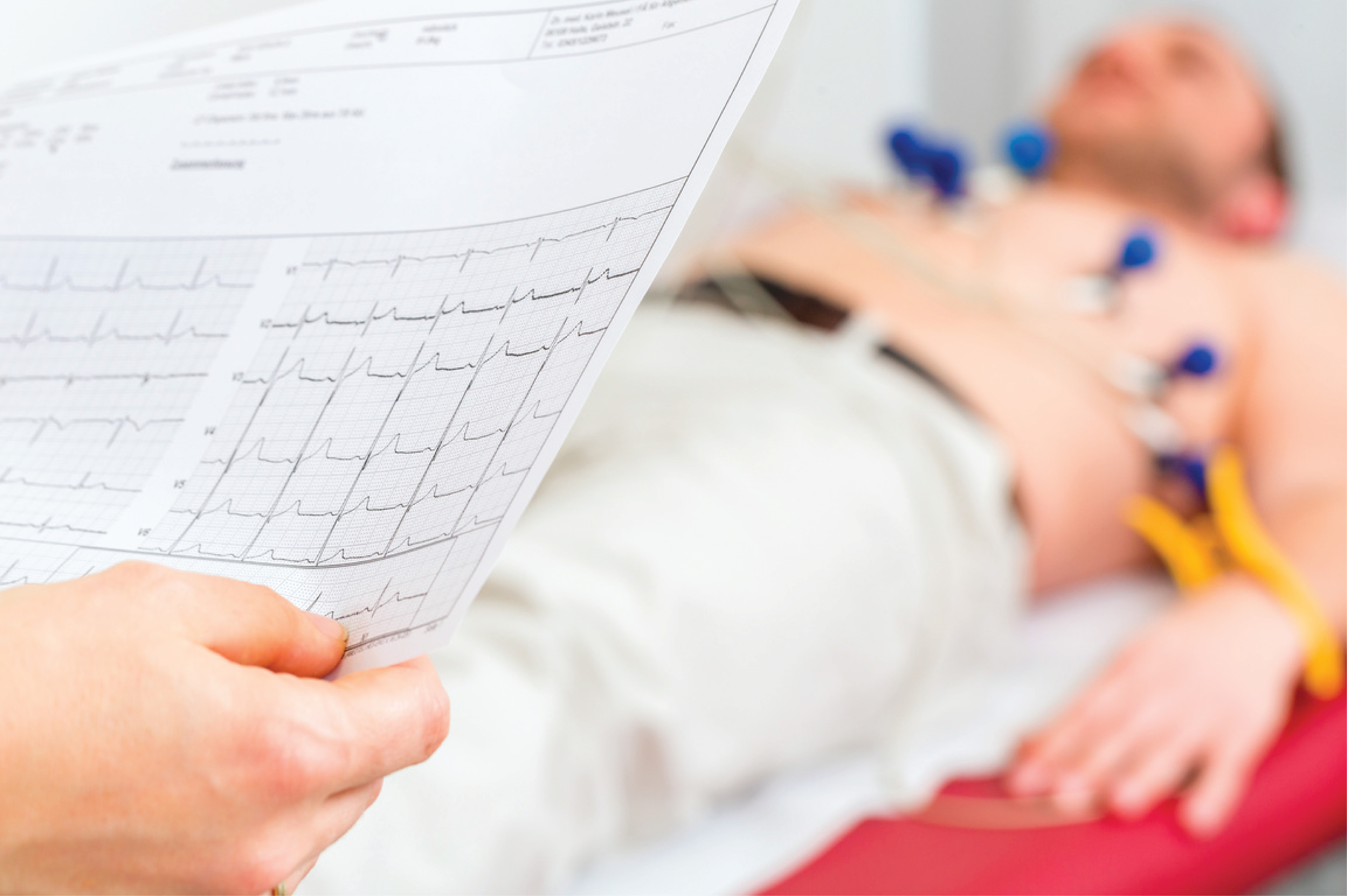
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG)
- Blood tests
- Coronary angiogram
- Echocardiogram
- Myocardial perfusion imaging
- Computerized tomography (CT) angiogram
- Stress test
Treatment
- Clot busters help break up a blood clot that's blocking an artery. These drugs also are known as thrombolytics.
- Nitroglycerin improves blood flow by temporarily widening blood vessels.
- Anti-platelet drugs help prevent blood clots from forming.
- Statins lower the amount of cholesterol in the blood.
- Cardiac catheterization to diagnosis and remove blockage